Disaster Prevention Resources
Landslide Preparedness
Previous erosion disaster information is here |
When it has continued raining for a long time, be careful of erosion disasters!
|
When it has continued raining for a long time, the ground may become soft, and sediment disasters (such as rockslides, landslides, and mudslides.) are more likely to occur.
|
Rockslides occur when the ground becomes soft due to heavy rain or earthquakes, and suddenly collapses. The collapsed rocks and sand may travel 2-3 times the distance of the slope height.
Areas prone to rockslides characteristically have more occurances of rockslides than other erosion-related disasters. There are 86,651 such sites across Japan (based on a survey carried out in 1997).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
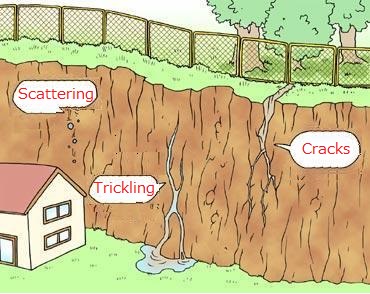
Rockslides Precursor Phenomena
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
-
When small rocks start to fall from cliffs
-
When water starts to seep out of cliffs
-
When cracks form in cliffs
|
 Scattering
Trickling
Cracks
Scattering
Trickling
Cracks
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
A landslide occurs when rainwater, etc., seeps into a loose layer of land, such as clay, in a location with a gentle slope, resulting in the ground moving. A wide damage area, simultaneous damage to houses, fields, paddocks and the traffic network are characteristic of landslides.
The movement of a landslide is often invisible, at a few millimeters per day. However, there are instances when the ground suddenly moves a few meters. Also, if river water has been dammed by a landslide, it may cause major disasters downstream when released.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Landslide Precursor Phenomena
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
-
When well water becomes muddy
-
When the ground becomes cracked and part of it
subsides or swells
-
When there is a sudden change in the amount of
water in ponds or swamps
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
A mudslide occurs where soil and stones collapsed from a valley or mountain surface suddenly, flowing out along with water, usually after a long period of rain during the rainy season or rain from a typhoon. Mudslide disasters often occur where there is a rapidly flowing river or in an alluvial fan, and cause damage with their high speed and power.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mudslide Precursor Phenomena
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
-
When a rumbling sound is heard from the whole
mountain
(called “Yamanari” in Japanese)
-
When rivers are muddy or carry driftwood
-
When river water levels decrease, despite
continuing rain
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Previous erosion disaster information is here
|
When it has continued raining for a long time, be careful of erosion disasters!
|
When it has continued raining for a long time, the ground may become soft, and sediment disasters (such as rockslides, landslides, and mudslides.) are more likely to occur.
|
Rockslides occur when the ground becomes soft due to heavy rain or earthquakes, and suddenly collapses. The collapsed rocks and sand may travel 2-3 times the distance of the slope height.
Areas prone to rockslides characteristically have more occurances of rockslides than other erosion-related disasters. There are 86,651 such sites across Japan (based on a survey carried out in 1997).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rockslides Precursor Phenomena |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A landslide occurs when rainwater, etc., seeps into a loose layer of land, such as clay, in a location with a gentle slope, resulting in the ground moving. A wide damage area, simultaneous damage to houses, fields, paddocks and the traffic network are characteristic of landslides.
The movement of a landslide is often invisible, at a few millimeters per day. However, there are instances when the ground suddenly moves a few meters. Also, if river water has been dammed by a landslide, it may cause major disasters downstream when released.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Landslide Precursor Phenomena |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A mudslide occurs where soil and stones collapsed from a valley or mountain surface suddenly, flowing out along with water, usually after a long period of rain during the rainy season or rain from a typhoon. Mudslide disasters often occur where there is a rapidly flowing river or in an alluvial fan, and cause damage with their high speed and power.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Mudslide Precursor Phenomena |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Copyright(C) Mie Prefecture, All Rights Reserved.
Department of Disaster Prevention, Mie Prefecture